Protection
Protection against mass surveillance and spying. ShutUpTrackers is a socially motivated website that provides information for protecting your data security and privacy
Protection against mass surveillance and spying. ShutUpTrackers is a socially motivated website that provides information for protecting your data security and privacy
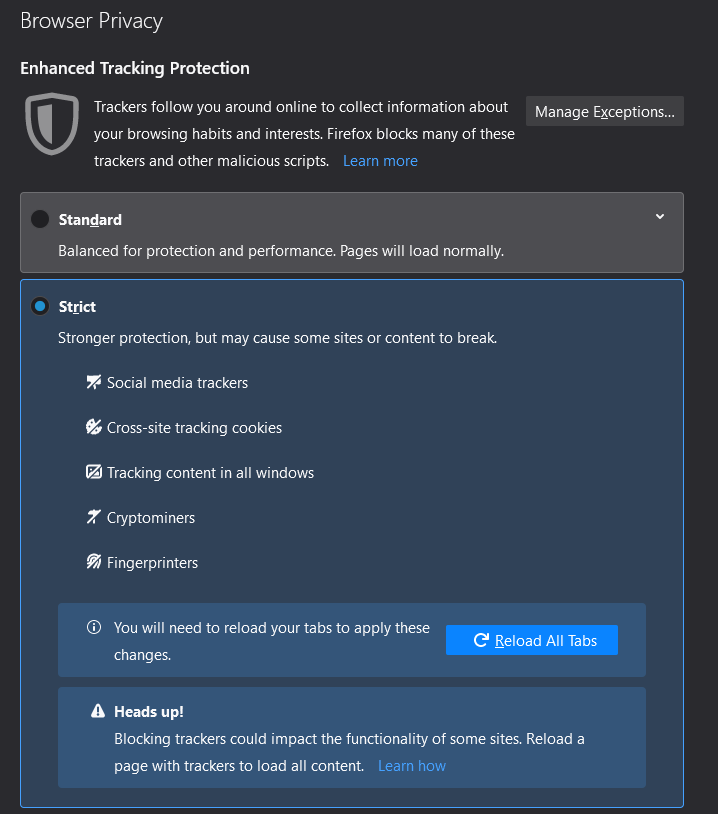
We will see the largest set of options, the Privacy and Security tab of Firefox. First, enhanced tracking protection.
This set of filters is set by default to Standard, but we will change it to Strict.
Also, in some rare cases, strict protections can cause websites to malfunction.
If you think that strict browsing protection is damaging a website you visit frequently, you can disable it site by site using the shield icon in the address bar.
Disabling Enhanced Tracking Protection will of course decrease your privacy on that site.
In the Search tab, change your default search engine to something other than Google, Bing, Yahoo ...
We offer various alternatives to these search engines here
When you use Firefox, the browser retrieves information about what you are doing, the type of extensions you have installed and many other things from your browser. Although they claim to do so from a privacy perspective, it is always best to send as little data as possible from a privacy perspective, so we will uncheck all boxes under "Firefox data collection and use" for security reasons.
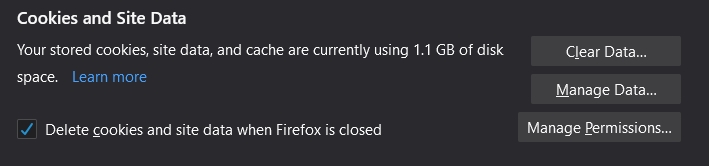
This one is for more advanced users, so if you don't understand what it does, you can skip this section. Firefox offers the ability to delete all your cookies and site data every time Firefox is closed. Cookies and site data are small pieces of information that sites store in your browser, and they have a multitude of uses. They are used for things like keeping you logged in and recording your website preferences, but they can also be used to track you on different websites. By regularly deleting your cookies, your browser will appear website specific, making it harder to track you.
The DNS (or Domain Name System) is what your browser uses to turn domain names like shutuptrackers.com into IP addresses like 185.193.126.127.
Since computers can only communicate with IP addresses, it is necessary to use DNS each time you visit a domain.
But the DNS is unencrypted by default, which means that everyone in your network (including your ISP) can see the domains you are looking for, and in some situations they can even modify IP responses to redirect you to their own websites!
Encrypting your DNS traffic can protect your queries and add extra protection to your browsing.
Encrypted DNS takes many forms: DNS over HTTPS (DoH), DNS over TLS, DNSCrypt, etc., but they all accomplish the same thing.
They keep your DNS queries private from your ISP, and they make sure they aren't tampered with in transit between your DNS provider.
Fortunately, Firefox recently added native DoH support to the browser. On the General page of your preferences, scroll down to and open Network Settings.
At the bottom of the window you will be able to select "Enable DNS over HTTPS" and choose a provider:

It should also be noted that even with DoH, your ISP will still be able to see what domain you're connecting to because of a technology called Server Name Indication (SNI). Until SNI is encrypted as well, there's no getting around it. Encrypted SNI (eSNI) is in the works — and can actually be enabled on Firefox today — but it only works with a small number of servers, mainly ones operated by Cloudflare, so its use is limited currently. Therefore, while DoH provides some additional privacy and integrity protections, its use as a privacy tool is limited until other supplemental tools like eSNI and DNSSEC are finalized and implemented.
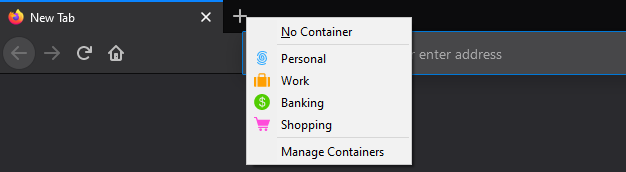
Mozilla has an in-house add-on called Multi-Account Containers that allows you to isolate websites from each other. For example, you could have Facebook in a container separate from your other browsing. In this situation, Facebook would only be able to set cookies with your profile on sites within the container, keeping your other browsing protected.
First you need to go to about:config and press "Accept the Risk and Continue".
privacy.trackingprotection.fingerprinting.enabled = true
Blocks Fingerprinting
privacy.firstparty.isolate = true
This preference isolates all browser identifier sources (e.g. cookies) to the first party domain, with the goal of preventing tracking across different domains. (Don't do this if you are using the Firefox Addon "Cookie AutoDelete" with Firefox v58 or below.)
privacy.resistFingerprinting = true
This preference makes Firefox more resistant to browser fingerprinting.
privacy.trackingprotection.cryptomining.enabled = true
Blocks CryptoMining
privacy.trackingprotection.enabled = true
This is Mozilla's new built-in tracking protection. One of it's benefits is blocking tracking (i.e. Google Analytics) on privileged pages where add-ons that usually do that are disabled.
browser.send_pings = false
The attribute would be useful for letting websites track visitors' clicks.
browser.urlbar.speculativeConnect.enabled = false
Disable preloading of autocomplete URLs. Firefox preloads URLs that autocomplete when a user types into the address bar, which is a concern if URLs are suggested that the user does not want to connect to.
dom.event.clipboardevents.enabled = false
Disable that websites can get notifications if you copy, paste, or cut something from a web page, and it lets them know which part of the page had been selected.
media.eme.enabled = false
Disables playback of DRM-controlled HTML5 content, which, if enabled, automatically downloads the Widevine Content Decryption Module provided by Google Inc.
DRM-controlled content that requires the Adobe Flash or Microsoft Silverlight NPAPI plugins will still play, if installed and enabled in Firefox.
media.gmp-widevinecdm.enabled = false
Disables the Widevine Content Decryption Module provided by Google Inc., used for the playback of DRM-controlled HTML5 content.
media.navigator.enabled = false
Websites can track the microphone and camera status of your device.
network.cookie.cookieBehavior = 1
Disable cookies
0 = Accept all cookies by default
1 = Only accept from the originating site (block third-party cookies)
2 = Block all cookies by default
network.http.referer.XOriginPolicy = 2
Only send Referer header when the full hostnames match.
0 = Send Referer in all cases
1 = Send Referer to same eTLD sites
2 = Send Referer only when the full hostnames match
network.http.referer.XOriginTrimmingPolicy = 2
When sending Referer across origins, only send scheme, host, and port in the Referer header of cross-origin requests.
0 = Send full url in Referer
1 = Send url without query string in Referer
2 = Only send scheme, host, and port in Referer
webgl.disabled = true
WebGL is a potential security risk.
browser.sessionstore.privacy_level = 2
This preference controls when to store extra information about a session: contents of forms, scrollbar positions, cookies, and POST data.
0 = Store extra session data for any site. (Default starting with Firefox 4.)
1 = Store extra session data for unencrypted (non-HTTPS) sites only. (Default before Firefox 4.)
2 = Never store extra session data.
beacon.enabled = false
Disables sending additional analytics to web servers.
browser.safebrowsing.downloads.remote.enabled = false
Prevents Firefox from sending information about downloaded executable files to Google Safe Browsing to determine whether it should be blocked for safety reasons.
Disable Firefox prefetching pages it thinks you will visit next:
Prefetching causes cookies from the prefetched site to be loaded and other potentially unwanted behavior.
network.dns.disablePrefetch = true
network.dns.disablePrefetchFromHTTPS = true
network.predictor.enabled = false
network.predictor.enable-prefetch = false
network.prefetch-next = false
network.IDN_show_punycode = true
Not rendering IDNs as their Punycode equivalent leaves you open to phishing attacks that can be very difficult to notice.
WebRTC is a communication protocol that works with JavaScript that can leak your IP address from behind your VPN.
Here are two different ways to disable WebRTC :
- Firstly, the simplest one, you will just have to install this extension named Disable WebRTC
- Another method that requires a little more effort, you need to go to about:config and press "Accept the Risk and Continue".
Then you have to search for media.peerconnection.enabled and set it to false
Note: This disables browser-based call functionality that is used for webapps like Discord, etc.